INCOSE Handbook Structure and Methods
INCOSE adopts and expands upon the systems engineering processes described in ISO/IEC/IEEE 15288. INCOSE does not define new processes, rather it provides amplifying information on the application of the processes defined in 15288 (INCOSE 2015). Figure 1.1 is adopted from INCOSE 2015 which itself is adopted from (ISO/IEC/IEEE 15288).
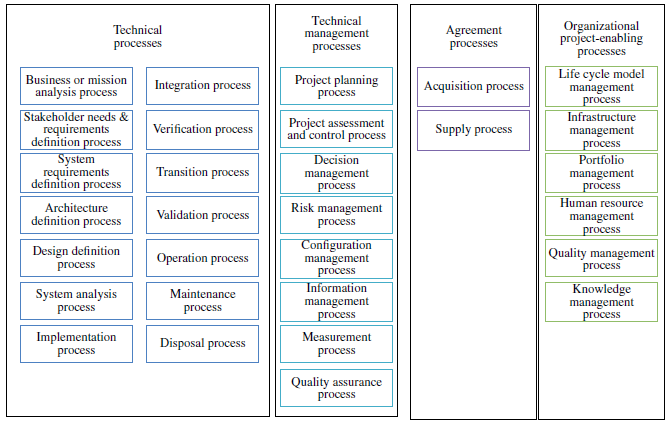
CABOKtip: The 15288 Agreement Process area is similar to the PMBOK Project Procurement Management Knowledge Area which includes the process areas: Plan Procurement Management, Conducting Procurement and Controlling Procurement knowledge areas within the PMI Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBoK) (PMI 2017).
CABOKtip: The Organizational Process Area area is analogous to the Organizational Process Assets within the PMBoK (PMI 2017).
The INCOSE SE Handbook uses Function models to depict each process along with its inputs, outputs, mechanisms and constraints. The models are consistent with IDEF0 Activity Diagrams and Input/Process/Output (IPO) Models often used in process improvement and leaning methods. This diagramming approach is an effective way of visualizing a process from the top level. Figure 1.2 represents the Input, Process, Output Model structure used by INCOSE to introduce each process in the handbook (INCOSE 2015).
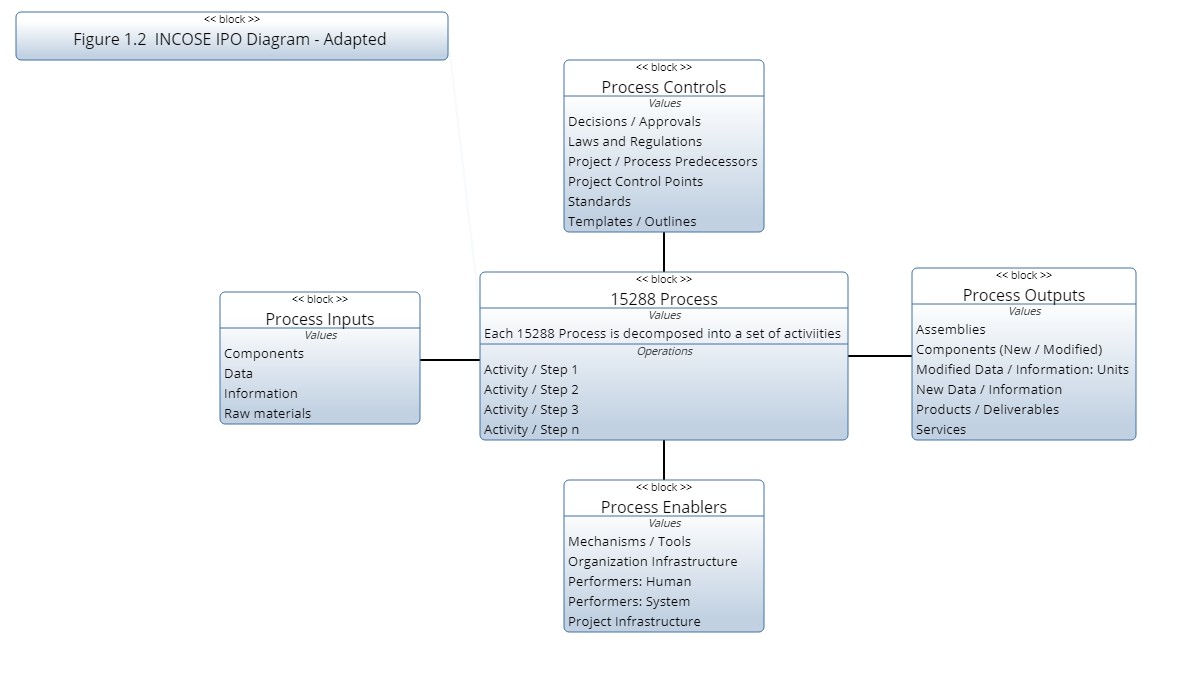
The block in the center of the diagram represents and activity or function performed in a process. Each activity / function can have one or more Inputs, Outputs, Mechanisms and Constraints.
Inputs are items that are modified or consumed by the activity / function. (Raw material, components, assemblies, data or information)
Outputs are items resulting from the activity / function: new components, assemblies, data or information. Inputs do not normally pass through an activity without being modified.
Controls are items that influence or direct how the activity is to be performed. These directions may be in the form of specifications for developing the outputs, or regulations governing the process. Regulations include safety considerations or environmental policy and design specifications define the structure or characteristics of the output.
CABOKtip: Please refer to Activity / Function Models for more information.