Introduction
This article provides introduction and overview of the Guide to the Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK). (SEBoK) was created by the Body of Knowledge and Curriculum to Advance Systems Engineering (BKCASE) project. BKCASE is overseen by a Governing Board, consisting of the International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE), the Systems Engineering Research Center (SERC), and the IEEE Computer Society. SEBoK is published electronically at http://sebokwiki.org/wiki/Guide_to_the_Systems_Engineering_Body_of_Knowledge_(SEBoK)
The goal of this article is to establish for the reader awareness of the publication and its contents as a significant source of information on systems engineering.
Citation Information:
When citing the SEBoK in general:BKCASE Editorial Board. 2017. The Guide to the Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK), v. 1.9. R.D. Adcock (EIC). Hoboken, NJ: The Trustees of the Stevens Institute of Technology. Accessed DATE. www.sebokwiki.org. BKCASE is managed and maintained by the Stevens Institute of Technology Systems Engineering Research Center, the International Council on Systems Engineering, and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Computer Society.
To cite a specific article within the SEBoK:
SEBoK Authors. "Article Title." in BKCASE Editorial Board. 2017. The Guide to the Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK), v. 1.9. R.D. Adcock (EIC). Hoboken, NJ: The Trustees of the Stevens Institute of Technology. Accessed DATE. www.sebokwiki.org. BKCASE is managed and maintained by the Stevens Institute of Technology Systems Engineering Research Center, the International Council on Systems Engineering, and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Computer Society.
Further information can be found at the SEBoK Citations Page: http://sebokwiki.org/wiki/Cite_the_SEBoK
Overview
The SEBoK is intended to provide guidance on the range of topics contained in the discipline of systems engineering and gives an organizational concept for structuring the information. The purpose of the SEBoK is not to contain all information for systems engineering, but instead to provide an overview of the breadth of the discipline in context, with pointers to relevant sources for additional detail.
Methods
The SEBoK is published in Wiki format where all information is published digitally allowing navigation vertically and horizontally using embedded hyperlinks. The SEBoK currently composed of seven sections. Each section is further arranged by several knowledge areas germane to the purpose of the section. The hyperlinks are embedded in the text, as article table of contents and as navigation graphics. Figure 1 is adopted from SEBoK which has hyperlinks embedded in each section of the graphic.
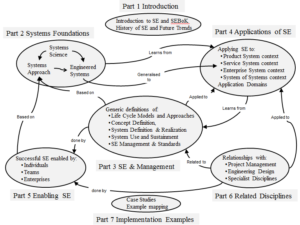
BoK Organization
- Part 1 – An introduction to the main concepts of the SEBoK as well as the organization and uses of the SEBoK itself.
- Part 2 – An overview of the concepts of systems science and their relevance to systems engineering.
- Part 3 – The most traditional systems engineering knowledge, including life cycle concepts, the processes that support systems engineering activities, systems engineering management considerations, and key standards.
- Part 4 – The application of the more general principles in Part 3 to specific types of systems, specifically products, services, enterprises, and systems of systems.
- Part 5 – A discussion of the principles needed to organize to perform systems engineering at the organization, team, and individual levels.
- Part 6 – A discussion of several disciplines relevant to systems engineering, such as project management, engineering management, design engineering including software engineering, and industrial engineering, but also including specialty engineering areas
- Part 7 – Real-world examples of systems engineering achievements and challenges.
Important Topics
Introduction to Systems Engineering (Section 1)
Knowledge Areas within the Section:
- Systems Engineering Overview
- Economic Value of Systems Engineering
- Systems Engineering: Historic and Future Challenges
- Systems Engineering and Other Disciplines
Introduction to SE Transformation (Section 1)
Knowledge Areas within the Section:
- Transitioning Systems Engineering to a Model-based Discipline
- Systems Engineering Core Concepts
- SEBoK Users and Use Cases
Introduction to SE Transformation (Section 1)
Knowledge Areas within the Section:
- Transitioning Systems Engineering to a Model-based Discipline
- Systems Engineering Core Concepts
SEBoK Users and Use Cases (Section 1)
Systems Fundamentals (Section 2)
- What is a System?
- Types of Systems
- Groupings of Systems
- Complexity
- Emergence
Systems Science (Section 2)
- History of Systems Science
- Systems Approaches
Systems Thinking (Section 2)
- What is Systems Thinking?
- Concepts of Systems Thinking
- Principles of Systems Thinking
- Patterns of Systems Thinking
Representing Systems with Models (Section 2)
- What is a Model?
- Why Model?
- Types of Models
- System Modeling Concepts
- Modeling Standards
- Integrating Supporting Aspects into System Models
Systems Approach to Applied Engineering (Section 2)
- Overview of the Systems Approach
- Engineered System Context
- Identifying and Understanding Problems and Opportunities
- Synthesizing Possible Solutions
- Analysis and Selection between Alternative Solutions
- Implementing and Proving a Solution
- Deploying, Using, and Sustaining Systems to Solve Problems
- Stakeholder Responsibility
- Applying the Systems Approach